How to Test AI LLM Prompts

In the rapidly evolving landscape of AI development, Large Language Models have become fundamental building blocks for modern applications. Whether you're developing chatbots, copilots, or summarization tools, one critical challenge remains consistent: how do you ensure your prompts work reliably and consistently?
The Challenge with LLM Testing
LLMs are inherently unpredictable – it's both their greatest feature and biggest challenge. While this unpredictability enables their remarkable capabilities, it also means we need robust testing mechanisms to ensure they behave within our expected parameters. Currently, there's a significant gap between traditional software testing practices and LLM testing methodologies.
Current State of LLM Testing
Most software teams already have established QA processes and testing tools for traditional software development. However, when it comes to LLM testing, teams often resort to manual processes that look something like this:
- Maintaining prompts in Google Sheets or Excel
- Manually inputting test cases
- Recording outputs by hand
- Rating responses individually
- Tracking changes and versions manually
This approach is not only time-consuming but also prone to errors and incredibly inefficient for scaling AI applications.
A Better Approach to LLM Testing
1. Structured Testing Interface
The familiar spreadsheet interface remains a good starting point – it's intuitive and accessible. However, modern LLM testing needs to go beyond basic spreadsheet functionality. An effective testing interface should:
- Support multiple LLM providers (OpenAI, Anthropic, Google Gemini, Mistral)
- Enable batch testing
- Provide version control
- Offer automated result recording
2. Deterministic Testing
The most straightforward and cost-effective testing approach is deterministic testing. These tests are:
- Fast to execute
- Free from additional API costs
- Perfect for specific use cases
Example Use Cases:
- Sentiment Classification: Checking if "I'm very happy" returns a positive sentiment
- JSON Structure Validation: Ensuring outputs maintain correct formatting
- Specific Word or Phrase Presence: Checking for required elements in responses
3. LLM-as-Judge Testing
For more complex scenarios where deterministic testing falls short, LLM-as-Judge testing provides a sophisticated solution. This approach leverages another language model to evaluate responses, offering nuanced assessment capabilities that would be difficult or impossible to achieve through traditional testing methods.
How LLM-as-Judge Works
The process involves three key components:
- The original prompt and its response
- Your specific evaluation criteria
- A separate LLM that acts as an impartial judge
The judge LLM receives both the original context (input and output) and your evaluation criteria, then provides a structured assessment based on your specified scoring system.
Key Evaluation Capabilities
1. Response Quality Assessment
- Relevance to the original query
- Accuracy of information
- Completeness of the answer
- Logical flow and coherence
- Adherence to given context
2. Safety and Compliance Checks
- Toxicity detection
- Bias identification
- PII (Personal Identifiable Information) detection
- Compliance with business rules
- Inappropriate content filtering
3. RAG-Specific Evaluation
- Verification of source material usage
- Assessment of information synthesis
- Checking for hallucinations
- Context retention accuracy
- Citation accuracy
Scoring Types and Their Applications
1. Boolean Scoring (Yes/No)
- Best for clear-cut criteria
- Example: "Does the response contain any PII?"
- Useful for pass/fail requirements
2. Scale Scoring (A to E)
- Provides nuanced quality assessment
- Example grading scale:
- A: Exceptional response, exceeds requirements
- B: Strong response, meets all requirements
- C: Acceptable response with minor issues
- D: Problematic response needing improvement
- E: Failed to meet basic requirements
3. Classification Categories
- Flexible categorization system
- Example categories for sentiment analysis:
- Positive
- Negative
- Neutral
- Mixed
- Customizable based on use case
Writing Effective Evaluation Criteria
To get the most out of LLM-as-Judge testing, consider these best practices:
1. Be Specific
Poor criteria: "Check if the response is good" Good criteria: "Evaluate if the response: - directly answers the user's question - uses information from the provided context - maintains a professional tone"
2. Break Down Complex Requirements
Instead of: "Check for quality" Use: - Check for factual accuracy - Verify logical flow - Assess completeness - Evaluate clarity
3. Include Context-Specific Guidelines
Example: "For technical documentation responses, ensure: - All technical terms are accurately used - Code examples are syntactically correct - Explanations are suitable for the specified expertise level"
Cost and Performance Considerations
While LLM-as-Judge testing provides powerful evaluation capabilities, it's important to consider:
- Costs: Each evaluation requires an additional LLM API call
- Time: Testing takes longer than deterministic methods
- Reliability: Judge LLMs may have their own biases or limitations
Best practices for managing these considerations:
- Use deterministic tests for simple cases
- Reserve LLM-as-Judge for complex evaluations
- Batch test when possible
- Cache results for identical scenarios
Integration with Testing Workflow
LLM-as-Judge testing works best as part of a comprehensive testing strategy:
- Start with deterministic tests for basic requirements
- Apply LLM-as-Judge for nuanced evaluation
- Use results to improve prompt engineering
- Track patterns in evaluation results
- Continuously refine evaluation criteria
Real-World Success: Deepnote Case Study
Deepnote, a leading AI-powered data workspace, provides a perfect example of how proper LLM testing can transform development efficiency. When launching their AI assistant for notebook blocks, they faced a common challenge: ensuring AI outputs remained contextually relevant and effectively solved user problems.
Initially, their team spent days manually fine-tuning prompts for complex use cases. After implementing Langtail, they adopted a data-driven, systematic approach to AI testing and development. The results were significant:
- Hundreds of hours saved in development time
- Increased developer confidence in prompt modifications
- More accurate and consistent LLM outputs
- Streamlined testing process
This case study demonstrates how structured testing can transform LLM development from a time-consuming manual process to an efficient, systematic approach.
Building Reliable LLM Applications
To create more predictable LLM applications, consider implementing this testing workflow:
1. Offline Testing
- Develop comprehensive test suites
- Run deterministic tests first
- Add LLM-as-judge tests for complex scenarios
2. Production Monitoring
- Implement logging and observability
- Track real-world interactions
- Identify edge cases and failures
3. Continuous Improvement
- Add failed cases to test suite
- Refine prompts based on real data
- Verify improvements don't cause regressions
4. Model Evaluation
- Test new LLM models against existing test suites
- Compare performance metrics
- Evaluate cost-benefit trade-offs
Introducing Langtail: Streamlined LLM Testing
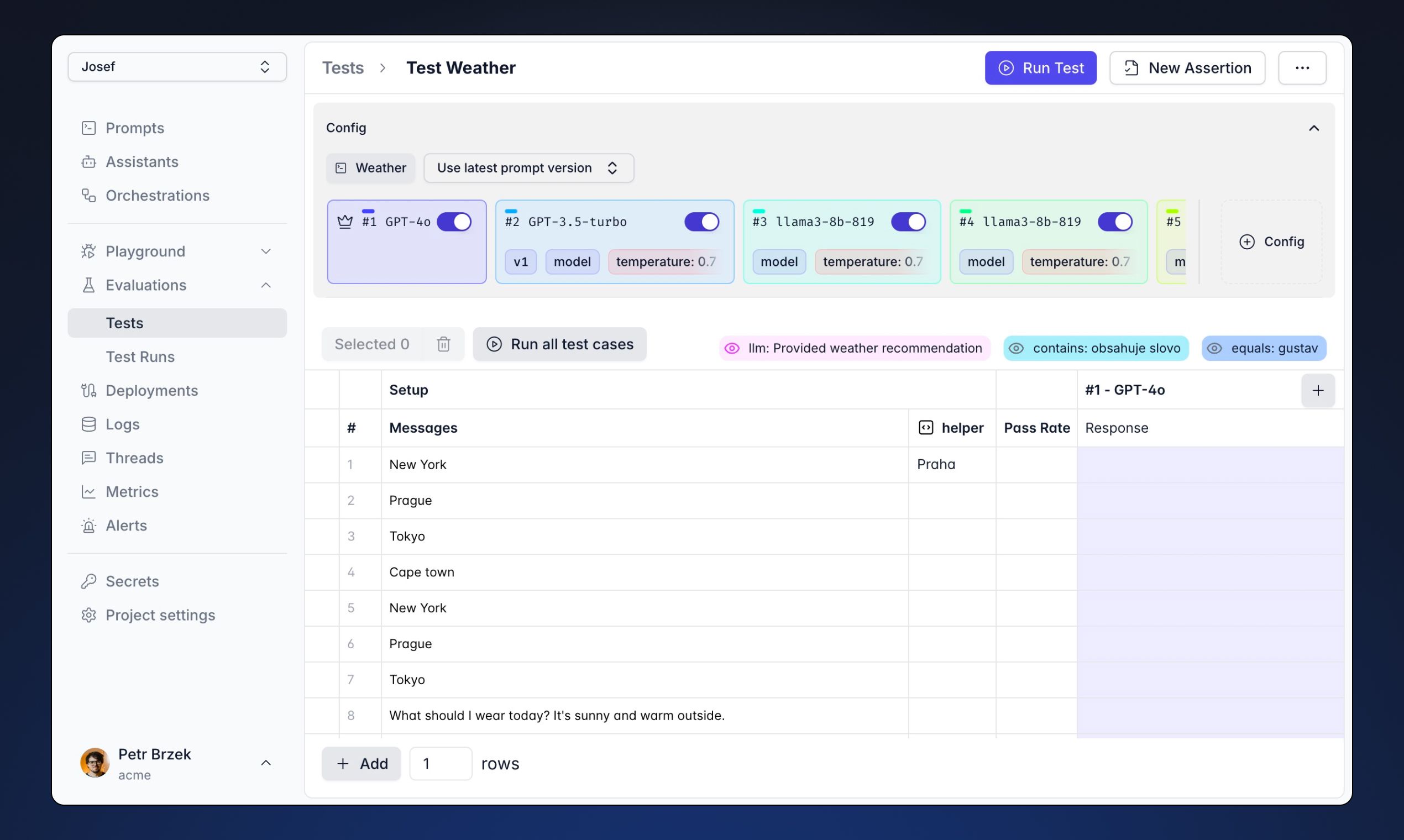
At Langtail, we've developed a solution that addresses these testing challenges. Our platform offers:
- Intuitive spreadsheet-like interface
- Support for multiple LLM providers
- Automated test execution
- Comprehensive assertion types
- Production monitoring
- Test suite management
Getting Started with Langtail
We understand that transitioning to a new testing framework can be challenging. That's why we offer:
- Personalized onboarding
- Documentation and best practices
- Support for existing test migration
- Custom integration assistance
Conclusion
As LLMs continue to become more integral to software applications, having robust testing practices is no longer optional. By implementing structured testing approaches and utilizing appropriate tools, teams can build more reliable AI applications while maintaining development efficiency. As demonstrated by Deepnote's success, the right testing approach can significantly impact development efficiency and output quality.
Ready to improve your LLM testing process? Try Langtail today and experience the difference structured testing can make in your AI development workflow.
Related Articles

What Can LLM APIs Be Used For? A Complete Guide with Examples
Discover all practical uses of LLM APIs, from content creation to automation. Learn how to implement LLM APIs in your projects with real examples and step-by-step guides.
Understanding LLM Chat Streaming: Building Real-Time AI Conversations
Learn how to implement streaming responses with Large Language Models for a more engaging and responsive chat experience.
What is the Best Way to Think of Prompt Engineering
A comprehensive guide to understanding and mastering prompt engineering, exploring effective mental models and best practices for crafting AI prompts.




